A Focused Review of Dynamic Light Scattering
Exploring the particle size measurement landscape can be challenging and time-consuming. We have created a detailed review of industry-standard methods such as Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and image analysis, where we contrast the principles of DLS against image analysis. We have selected cutting-edge direct imaging particle size analysers, such as Eyecon2, to explain the fundamentals of image analysis which will give you an appreciation of some of the factors to consider in your choice of particle size distribution (PSD) analysis tools.
DLS, sometimes referred to as Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering (QELS) and Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (PCS), is an optical method of determining particle size properties within a disperse sample by observing the change in scattered light intensity as a function of time.
How Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) works
The fundamental principle governing the determination of particle size by DLS is interference. When two waves interact, they can combine in such a manner that the resultant wave is either an amplified or diminished superposition of the initially interacting waves, as is presented in the figure below. When the scattered waves interference is constructive, the DLS detector records high light intensity; and equally, when waves interference is destructive, the detector records low light intensity.
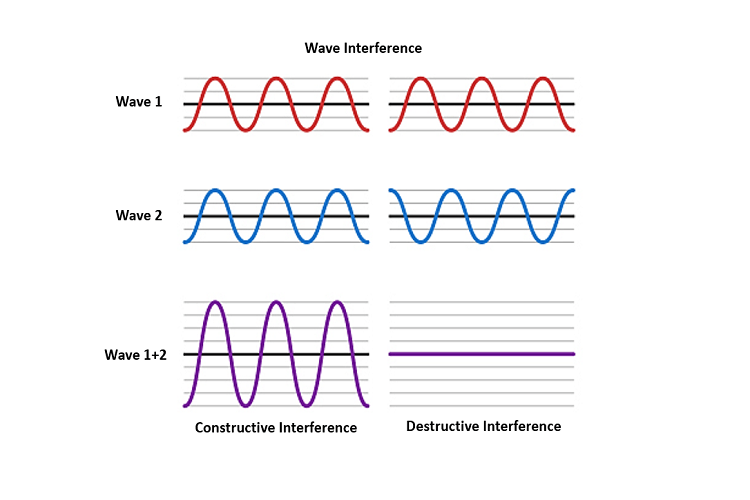
Therefore, given the large light intensity associated with DLS setups, many photons can interfere both constructively and destructively due to the many possible scattering angles. If this process were to be imaged, a speckle pattern would be observed, where various areas of bright and dark spots represent the constructive (bright spots) and destructive (dark spots) regions.
Our in-house advanced particle size analyser, Eyecon2, calculates particle size distributions, and shape information based on the measurement of individual particles within a sample image. The images captured are processed by the software EyePASS™ where the particle detection algorithm identifies and measures individual particles within the image.
Correlation with Particle Properties
The initial step of DLS is extracting the particle information and monitoring the change in the scattered intensity over time at a high temporal resolution, on the order of nano to a millisecond, and determine the correlation of the changing signal to itself to form a distribution. The application of the Mie theory can then be used to determine approximate particle volume and several other parameters.
Eyecon2 identifies particles within a sample image which are then processed by EyePASS. EyePASS uses a particle detection algorithm to identify and measure individual particles within the captured image. This approach results in a tighter volume fit than the cubed diameter of an equivalent circle fit used in many other image analysis systems. This allows Eyecon2 to more accurately calculate particle volume, which will affect the subsequently calculated D-Values.
Limitations
With any analytical method, there exist several difficulties and limitations. The following limitations apply to DLS and direct imagining particle size analysers:
DLS:
- Sample analysis is time-consuming
- It is limited to offline and at-line methods of use
- Low resolution in identification of closely-spaced multimodal size distributions
- Multiple light scattering when one particle is scattered by another before reaching the detector hinders accurate calculation of particle size
- Cannot be used for particle sizes greater than 2µm
- Very sensitive to temperature, solvent viscosity, and refractive index
- Sensitive to contamination, e.g., from dust
Direct image analysis:
- The focal length of the system may be limited, meaning samples must be adequately close to be measurable
- The measurement system may also be insensitive to very dark, shiny or transparent materials and may lead to an inability to achieve a representative measurement
- Cannot measure particle sizes below 50 µm
For more information, view our detailed application note where we deep dive further into DLS and many more industry-standard PSD measurement methods.
We at InnoGlobal Technology (formerly Innopharma Technology) are motivated to push boundaries in the pharmaceutical industry and share our knowledge. Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for more exciting developments from R&D to Industry 4.0!

